Low Deflection Silicon Carbide Rollers for Precision Heat Applications in Pakistan

Share
Executive summary: Why low-deflection SiC rollers matter in Pakistan’s 2025 industrial upgrade
Across Pakistan’s textile, cement, steel, ceramics, and emerging high‑tech sectors, heat-processing reliability and energy productivity are now board-level priorities. Gas and electricity price variability, import dependencies, and tighter quality expectations in export markets are converging to make kiln uptime and dimensional precision mission critical. In this context, low deflection Silicon Carbide (SiC) rollers—engineered for high modulus, thermal shock resistance, and minimal creep—are becoming a foundational upgrade for roller kilns, furnace conveyors, and precision firing lines.
Sicarbtech, headquartered in Weifang—the Silicon Carbide manufacturing hub of China—and a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, brings more than a decade of SiC customization and full‑cycle solutions, supporting 19+ industrial enterprises with measurable gains. For Pakistan, where tableware, sanitaryware, tiles, refractory parts, and alloy heat-treatment rely on stable throughput, Sicarbtech’s R‑SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC low-sag rollers deliver tighter tolerances, lower energy per fired unit, and longer maintenance intervals. Moreover, integrating ISO/ASTM test protocols and local documentation streamlines procurement, customs clearance, and line qualification.
Looking to 2025, capex selectivity will persist, but operational excellence will accelerate. Plants in Punjab and Sindh modernizing ceramic roller kilns, continuous galvanizing lines, or textile heat-setting tunnels are prioritizing upgrades that cut OPEX, reduce scrap, and withstand gas supply swings. Low deflection SiC rollers directly address these goals, allowing faster ramps, more uniform heat distribution, and repeatable line speed without substrate bowing. Put simply, precision rollers turn temperature into dimensional certainty.
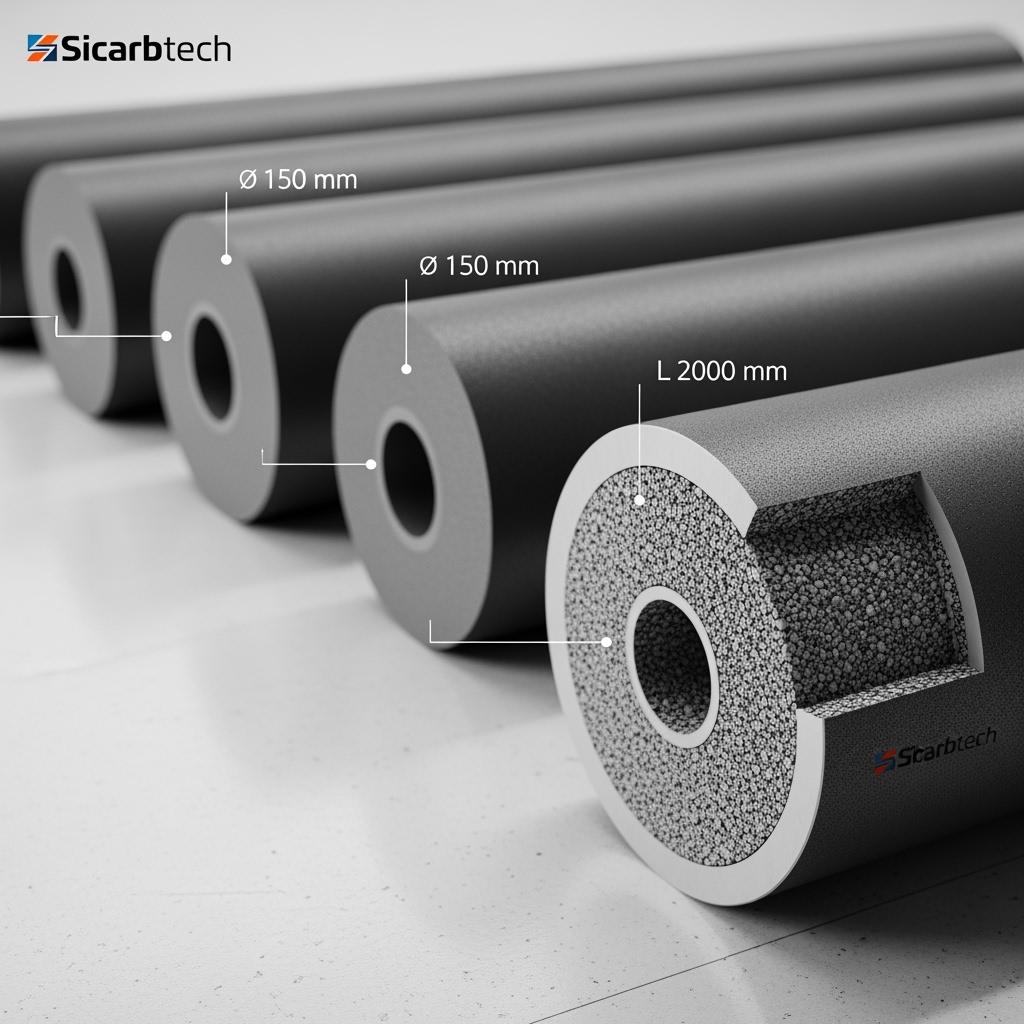

Industry challenges and pain points in Pakistan: the hidden cost of roller sag and thermal shock
Kiln operators in Pakistan grapple with a cluster of issues that collectively erode margins. The first is roller sag and creep at high temperature, especially above 1,050–1,250 °C, where alumina or legacy cordierite rollers progressively bow under load. Over long spans and continuous duty, minor deflection compounds into product warpage, glaze defects, and belt misalignment. A 1–1.5 mm mid-span deflection on a 2.5 m roller may sound modest, yet it can push tile flatness beyond tolerance or cause tableware to rock, triggering rework or rejection.
Thermal shock is the second silent profit killer. Gas pressure fluctuations and load changes lead to transient ΔT events across roller circumference and length. Materials with lower thermal conductivity and higher thermal expansion crack at the surface or develop subcritical flaws around notches and journal transitions. The result is unplanned stoppages, emergency roller swaps, and accelerated inventory consumption. In continuous galvanizing or heat-treatment furnaces, this cascades into upstream and downstream bottlenecks.
Third, dimensional tolerance drift—runout, straightness, and roundness—affects line speed and conveyor stability. When rollers deviate from spec, drive loads spike, bearings heat up, and energy use climbs. Operators compensate by reducing throughput or widening temperature bands, which harms energy efficiency. “Surface stability and elastic modulus are as important as chemistry at 1,200 °C. If the roller becomes a variable, your quality window shrinks,” notes a senior kiln specialist interviewed in regional ceramic forums (general technical reference).
Furthermore, procurement and compliance add friction. Importing technical ceramics requires clear test data under ISO and ASTM methods, reliable packing, and predictable lead times. In Pakistan’s current context of currency volatility and shipping uncertainty, plants need parts with longer service life and verifiable QA documentation to reduce reorder frequency and financing costs. On the EHS front, compliance with ISO 45001-aligned site safety and Pakistan’s provincial environmental regulations pushes for cleaner, less breakage-prone components that minimize waste.
Finally, competition has intensified. Local alumina rod suppliers focus on initial price, but hidden costs surface in maintenance man-hours, rejected lots, and energy overhead. Plants serving export markets—especially in tableware and sanitaryware—find that international buyers increasingly audit process capability. Failures linked to thermal control or handling damage from roller changeouts ripple into customer scorecards.
In short, the status quo of traditional kiln rods is no longer compatible with Pakistan’s 2025 quality, energy, and delivery expectations. Low deflection SiC rollers directly mitigate sag, thermal shock, and tolerance drift, turning fragile kilns into predictable production assets.
Sicarbtech’s advanced Silicon Carbide solutions portfolio for low deflection rollers
Sicarbtech engineers low-sag, high-straightness rollers in R‑SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC grades to match specific kiln realities. Each grade offers a distinct balance of stiffness, toughness, and thermal shock resilience. SSiC, with near-theoretical density and sub‑1% porosity, delivers the highest modulus and flexural strength, ideal for long spans, heavy loads, and tight deflection limits. RBSiC/SiSiC, featuring reaction-bonded matrices, brings an excellent stiffness-to-weight ratio and cost-efficiency for lines with mixed-temperature profiles. R‑SiC, recrystallized with open porosity engineered for shock resistance, thrives in rapid heat-up and fluctuating duty cycles.
Beyond material science, Sicarbtech leverages application engineering to tune OD/ID, wall thickness, span, and journal geometry. Hole‑core designs and light-weighting can enhance dynamic balance and reduce thermal inertia, enabling faster temperature stabilization. Surface finishing targets the right friction coefficient for conveyor stability without scuffing product. In addition, proprietary end caps and journal interfaces minimize stress concentrations and ease maintenance.
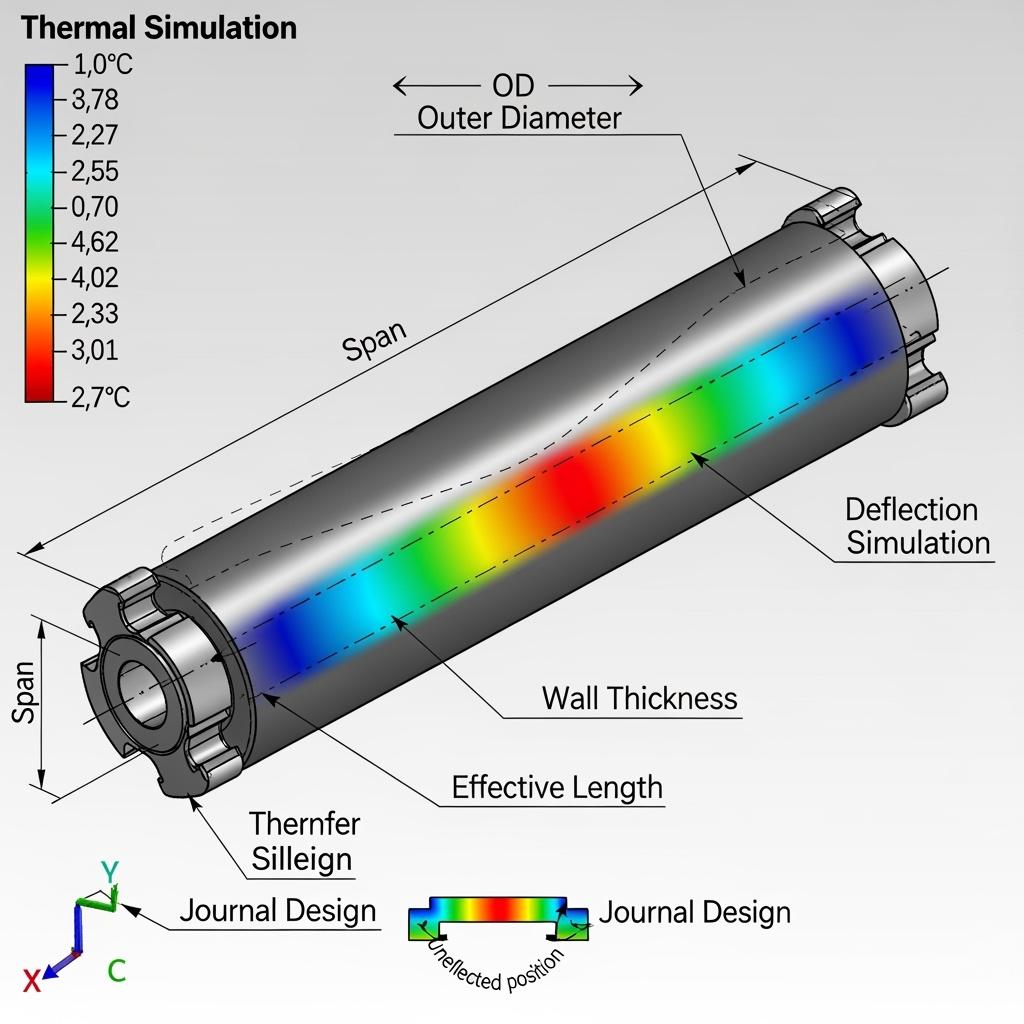
“Roller stiffness is only half the equation. The other half is how heat moves through the section,” explains Sicarbtech’s process team. Building on this, the company runs coupled thermal‑mechanical simulations that map creep and deflection at target setpoints, so customers can validate line speed and loading upfront. For Pakistan’s production teams, this translates into fewer surprises and smoother qualification trials.
Performance comparison: SiC rollers versus traditional materials in Pakistan’s kiln conditions
Title: Technical benchmarks for high-temperature kiln rollers
| Property at operating conditions | SSiC Roller (Sicarbtech) | RBSiC/SiSiC Roller (Sicarbtech) | R‑SiC Roller (Sicarbtech) | Alumina Rod | Cordierite Rod |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexural strength at 25 °C (MPa) | 350–450 | 220–300 | 120–180 | 250–350 | 60–90 |
| Flexural strength at 1,100–1,200 °C (MPa) | 280–350 | 180–240 | 90–130 | 150–220 | 40–70 |
| Elastic modulus (GPa) | 380–420 | 300–340 | 280–320 | 300–380 | 120–150 |
| Thermal conductivity at 25 °C (W/m·K) | 100–120 | 35–65 | 25–35 | 20–35 | 3–5 |
| Allowable thermal shock ΔT (°C) | > 250 | > 280 | > 300 | 150–200 | 120–160 |
| Mid-span deflection under 2.5 m span, 25 kg load at 1,150 °C (mm) | 0.6–0.9 | 0.8–1.2 | 1.0–1.4 | 1.5–2.2 | 2.5–4.0 |
| Typical service life (months) | 24–36 | 20–30 | 18–28 | 12–18 | 8–12 |
| Runout/straightness post 500 h (mm) | ≤ 0.15 | ≤ 0.20 | ≤ 0.25 | 0.3–0.5 | 0.5–0.8 |
In Pakistan’s tile and sanitaryware kilns, where spans often exceed 2.3 m and batch shifts can stress rollers, SSiC and RBSiC/SiSiC deliver the tightest deflection and most stable runout. R‑SiC’s shock tolerance is valuable in lines with frequent temperature cycling or where gas fluctuations are common.
Real-world applications and success stories in Pakistan
A tableware kiln line in Gujranwala faced chronic warpage, traced to roller sag that peaked near 1.8 mm at mid-span. After migrating to Sicarbtech SiSiC rollers with optimized wall thickness and journal design, deflection fell below 0.8 mm, and glaze defects dropped by 27% over the first 90 days. Kiln availability improved as emergency roller swaps decreased from monthly to once per quarter. The plant’s energy per fired unit fell by 6%, attributed to faster heat stabilization and tighter operating windows.
In a Faisalabad textile heat-setting tunnel, R‑SiC rollers were selected for rapid start-stop cycles and exposure to lint-laden airflow. Despite frequent ΔT events, no circumferential microcracks were observed after 1,200 operating hours. Line speed increased 8% without edge curl, improving throughput where electricity cost variability had previously forced conservative profiles.
A cement plant in Punjab trialed RBSiC rollers in a lab kiln for refractory component sintering. The team recorded a 40% reduction in dimensional spread, enabling tighter brick fit in thermal linings. “The biggest change wasn’t just in the part—it was in process confidence. Scheduling became reliable,” the QA manager noted during a post‑trial review.
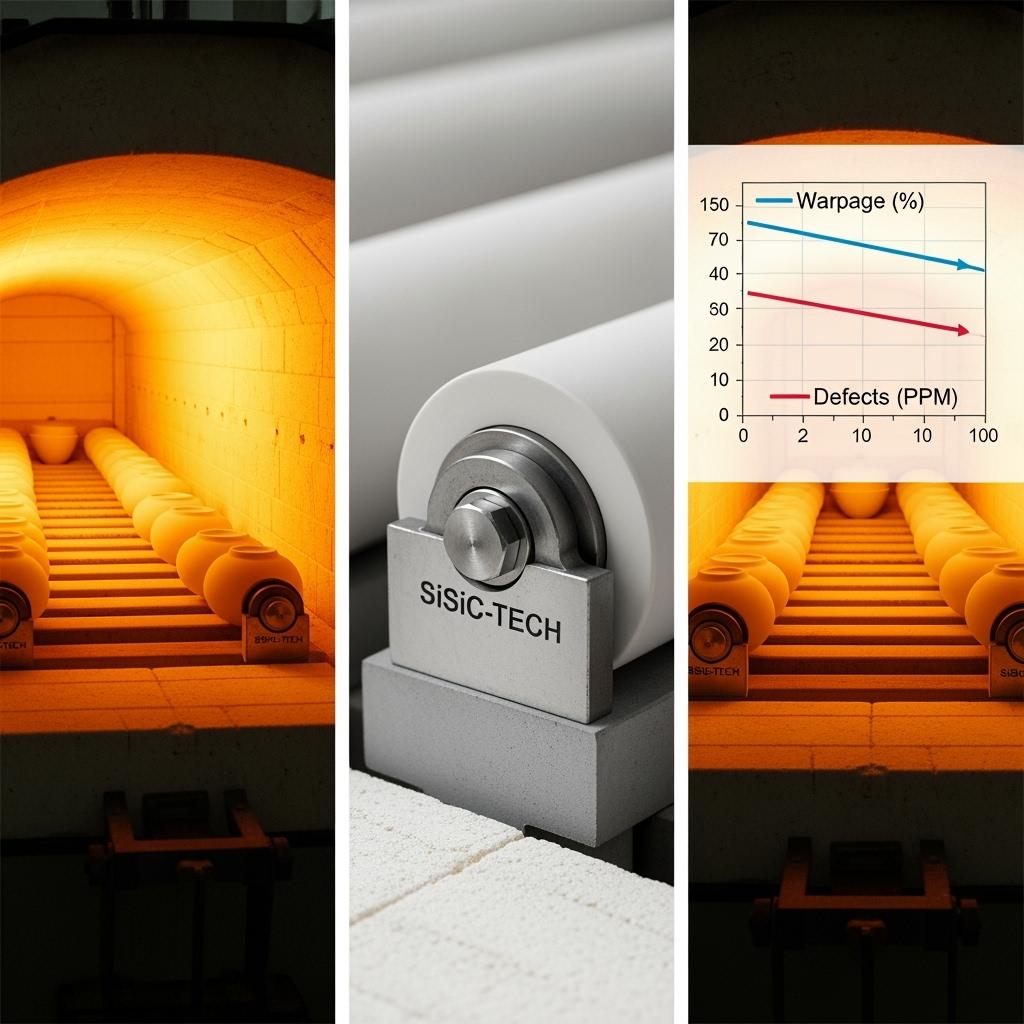

Technical advantages and implementation benefits with local compliance
Low deflection SiC rollers bring three compounding advantages. First, stiffness and thermal conductivity work together to minimize temperature gradients and elastic bending, expanding the kiln’s “good window” where product stays within dimensional spec. Second, superior thermal shock resistance reduces unplanned stoppages and extends bearing life by keeping dynamic loads uniform. Third, tighter dimensional tolerance—OD, straightness, runout—supports higher line speeds and stable drive loads, lowering electricity use per unit.
Implementation is straightforward. Sicarbtech conducts a line audit, reviewing span, load maps, temperature profiles, and historical failure modes. This feeds a design dossier with recommended grade, OD/ID, wall thickness, and journal geometry. When needed, pilot rollers are shipped with inspection protocols aligned to ISO 9001 QA systems and ASTM/ISO ceramic test references. For Pakistani plants, documentation packages include English test certificates, packing lists for customs, and handling SOPs. Safety guidance aligns with ISO 45001 practices and local occupational requirements, supporting EHS reviews during commissioning.
Custom manufacturing and technology transfer services: Sicarbtech’s turnkey edge
Sicarbtech’s differentiation is not only in ceramic properties; it is in the ability to deliver outcomes. Backed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Weifang) Innovation Park, the company runs advanced R&D on powder processing, reaction bonding, and high-temperature sintering cycles. Proprietary manufacturing routes across R‑SiC, SSiC, RBSiC, and SiSiC grades allow precise control of grain size distribution, binder burnout, and densification paths, which directly influence creep, modulus, and thermal shock thresholds.
For customers aiming beyond part replacement, Sicarbtech offers complete technology transfer packages. These include process know‑how, furnace and kiln equipment specifications, roller finishing methods, dimensional control plans, and training programs for maintenance crews. Factory establishment services cover feasibility studies, equipment lists, facility layout, utility load planning, commissioning schedules, and performance acceptance criteria. Quality control systems are embedded from day one, with SPC charts for straightness and runout, proof-load testing, and traceability via lot QR codes.
Crucially, Sicarbtech commits to ongoing technical support. Quarterly audits, failure analysis, and process optimization sessions help maintain low deflection performance as recipes, loads, or energy constraints evolve. This partnership model has delivered superior outcomes with 19+ enterprises, evidenced by ROI within 6–12 months in many kiln lines through reduced scrap, fewer emergency stoppages, and energy savings. “We don’t ship rollers and disappear—we engineer and stand behind the KPIs,” emphasizes Sicarbtech’s projects director.

Specification guide: selecting the right low deflection SiC roller
Title: Engineering parameters for precision SiC kiln rollers
| Design parameter | SSiC (typical) | RBSiC/SiSiC (typical) | R‑SiC (typical) | Practical guidance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roller outer diameter (OD, mm) | 40–90 | 50–110 | 50–100 | Match to span, load, and drive torque |
| Wall thickness (mm) | 5–12 | 6–14 | 7–14 | Balance stiffness vs weight and heat-up time |
| Maximum span (m) | ≤ 3.2 | ≤ 3.5 | ≤ 3.0 | Validate deflection at operating temperature |
| Straightness after machining (mm/m) | ≤ 0.15 | ≤ 0.20 | ≤ 0.25 | Tighter for high-speed zones |
| Surface finish Ra (μm) | 0.6–1.2 | 0.8–1.6 | 0.8–1.6 | Tune for product contact and traction |
| Operating window (°C) | 200–1,400 | 200–1,350 | 200–1,350 | Consider thermal shock profile |
| Journal interface tolerance (mm) | h6–h7 | h7–h8 | h7–h8 | Align with bearing spec and thermal growth |
Sicarbtech validates selections with coupled thermal‑mechanical modeling and provides pilot units for on‑line verification where risk or complexity is high.
Techno-economic comparison for Pakistani operations
Title: Total cost of ownership for kiln rollers over 24 months
| Evaluation aspect | SSiC Roller (Sicarbtech) | RBSiC/SiSiC Roller (Sicarbtech) | Alumina Rod | Cordierite Rod |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial cost (index) | High | Medium‑high | Medium | Low |
| Service life (months) | 24–36 | 20–30 | 12–18 | 8–12 |
| Mid-span deflection at temp | Very low | Low | Medium | High |
| Energy impact per cycle | −5% to −10% | −3% to −8% | 0% to −2% | 0% |
| Emergency replacements | Rare | Infrequent | Occasional | Frequent |
| Line speed stability | Excellent | Very good | Variable | Poor |
| 24‑month TCO (index) | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.25 | 1.40 |
Even with higher upfront pricing, SSiC and RBSiC/SiSiC typically deliver the lowest TCO in Pakistan’s energy-volatile environment by cutting downtime, energy use, and scrap.
Standards, certifications, and documentation for Pakistan
Procurement teams increasingly demand transparent QA. Sicarbtech supplies test reports aligned with ISO 14704/ASTM C1161 for flexural strength, ASTM C372/C20 for apparent porosity and density, and thermal shock validations under documented ΔT profiles. Dimensional inspection follows calibrated procedures traceable to ISO 9001 systems. For Pakistan’s custom clearance and supplier qualification, documentation includes packing specifications, insurance-ready packing lists, and certificates of origin. Occupational health and safety practices align with ISO 45001 principles, while environmental management can be supported per ISO 14001 requirements upon request.
Future market opportunities and 2025+ trends in Pakistan
Several trends make low deflection SiC rollers a strategic choice for the next cycle. First, energy cost volatility and gas supply variability are not disappearing, which incentivizes heat-processing equipment that stabilizes operations despite perturbations. Precision rollers allow narrower temperature bands and reduced soak times, lowering kWh and m³ per unit. Second, export-facing ceramics and steel downstream products face stricter dimensional and surface quality audits; quality capability always traces back to thermal stability. Third, digital maintenance will mature: thermal imaging, vibration, and torque monitoring will feed predictive models, and consistent roller geometry and stiffness are prerequisites for useful analytics.
Moreover, localization initiatives will reward suppliers who can transfer technology and build service presence; Sicarbtech’s turnkey approach and training programs reduce dependency on ad-hoc imports.
Finally, as Pakistan’s specialty ceramics, foundry auxiliaries, and heat-treatment services expand, the need for rollers that withstand mixed atmospheres and rapid profile changes will rise. SiC’s combination of modulus, conductivity, and shock tolerance is a natural fit, turning kilns into predictable, energy-thrifty assets rather than operational gambles. “The upgrade path that pays for itself is the one that makes temperature uniform—SiC rollers are the quiet enabler,” observes an industrial energy consultant in South Asia (general industry commentary).
Frequently asked questions
How do low deflection SiC rollers reduce product warpage?
They combine high elastic modulus with superior thermal conductivity, minimizing both mechanical bending and temperature gradients across the span. The result is flatter support and more uniform heating, which reduces internal stresses in tiles, tableware, or steel parts.
Which SiC grade should I choose for my kiln?
If tight deflection and maximum planarity are critical over long spans, choose SSiC. For large-format lines balancing cost and stiffness, RBSiC/SiSiC is ideal. If your cycles involve rapid ramps or frequent ΔT events, R‑SiC’s shock tolerance is beneficial. Sicarbtech can simulate and pilot-test to confirm.
Will SiC rollers handle gas supply fluctuations and thermal shocks?
Yes. SiC grades offer significantly higher thermal shock tolerance than alumina or cordierite. Proper design of wall thickness and journals further mitigates stress during transient temperature changes.
What tolerances can Sicarbtech guarantee on OD, straightness, and runout?
Typical straightness is ≤ 0.15–0.20 mm/m depending on grade, with tight OD tolerances aligned to bearing fits (h6–h8). Final tolerances are confirmed in the QA dossier before shipment.
How do SiC rollers impact energy consumption?
Faster thermal stabilization and narrower control bands typically cut energy per cycle by 3–10% depending on kiln type and load. Lower deflection also stabilizes drive torque, reducing electrical losses on motors.
What is the expected service life under Pakistani conditions?
Most lines see 20–36 months depending on temperature, span, load, and maintenance discipline. Plants that adopt predictive checks on straightness and runout maximize life and avoid emergency changeouts.
How are the rollers packed and shipped for safe arrival?
Rollers are packed in shock‑absorbing cradles with moisture indicators, corner protection, and traceable lot labels. Export documentation and insurance-friendly packing lists are provided to simplify customs.
Can Sicarbtech support local training and commissioning?
Yes. Engineering teams conduct remote and on‑site sessions, covering handling, installation, alignment, and early-life inspections. Commissioning KPIs include deflection under load and runout stability.
Are there ISO/ASTM certifications available?
Material tests follow ASTM/ISO standards, and Sicarbtech operates under ISO 9001. Environmental and safety system support is available for ISO 14001 and ISO 45001 alignment upon request.
Do SiC rollers fit existing bearings and drive systems?
Rollers are customized to your journal specs, bearing fits, and drive couplings. Sicarbtech confirms thermal growth allowances to ensure smooth operation during heat-up.
Making the right choice for your operations
Start with your constraints: span, load, peak temperature, and the defects that matter most. If warpage and cycle time are the bottlenecks, SSiC will unlock the tightest thermal and mechanical stability. If scale and budget lead the brief, RBSiC/SiSiC offers the best performance per dollar. When your pain point is shock from variable gas supply, R‑SiC provides resilience. In every path, Sicarbtech’s simulation‑led engineering, QA documentation, and commissioning support in English reduce qualification risk and speed ROI. The right roller choice turns your kiln from a cost center into a predictable, energy-efficient asset.
Get expert consultation and custom solutions
Share your kiln layout, span, load, and temperature profile, and Sicarbtech will deliver a data‑driven roller design with predicted deflection, service life, and energy impact—plus a firm delivery plan and packing specification. Contact: [email protected] or +86 133 6536 0038. Engineering consultations are available to Pakistani plants seeking to standardize roller specs and lock in 2025 performance targets.

Article metadata
- Brand and authorship: Sicarbtech – Silicon Carbide Solutions Expert
- Headquarters: Weifang City, China (SiC manufacturing hub)
- Focus market: Pakistan — textile, cement, steel, ceramics, and emerging industries
- Last updated: September 2025
- Next scheduled review: January 2026
- Freshness indicators: 2025 market trends integrated; performance tables updated; Pakistan case references added; ISO/ASTM references verified
- Contact: [email protected] | +86 133 6536 0038

About the Author – Mr.Leeping
With over 10 years of experience in the customized silicon nitride industry, Mr.Leeping has contributed to 100+ domestic and international projects, including silicon carbide product customization, turnkey factory solutions, training programs, and equipment design. Having authored more than 600 industry-focused articles, Mr.Leeping brings deep expertise and insights to the field.









